Indian scriptures – Vedas, Upanishad and Purana

Most of the Hindus do not have time to read their scriptures. Far from reading Vedas, and Upanishads, they don’t even read Gita whereas Gita can be read in 1 hour. However, in many places, they take out time to listen to the Bhagavata Purana or recite the unbroken recitation of the Ramayana or get the Satyanarayan Katha done at home. But you should know that Puranas, Ramayana, and Mahabharata are not the scriptures of Hindus, the scriptures are Vedas only.
The scriptures are divided into two parts – Shruti and Smriti. Vedas come under Shruti and the books of history and interpretation of Vedas, Puranas, Mahabharata, Ramayana, Smritis, etc. come under Smriti. The scriptures of the Hindus are the Vedas only. The essence of the Vedas is the Upanishads and the essence of the Upanishads is the Gita. Let’s know what is there in those books.
What’s in the Vedas?
Vedas are full of knowledge related to almost all the subjects like Brahma (God), Deities, Universe, Astrology, Mathematics, Chemistry, Medicine, Nature, Astronomy, Geography, Religious Rules, History, Sanskar, Customs, etc. There are 4 Vedas – Rigveda, Yajurveda, Samaveda and Atharvaveda. Rigveda’s Ayurveda, Yajurveda’s Dhanurveda, Samaveda’s Gandharvaveda, and Atharvaveda’s Sthapatyaveda have been described as Upavedas of the four Vedas respectively.

Rigveda
Rik means condition and knowledge. It has a lot to do with the geographical location and the mantras invoking the gods. The hymns of the Rigveda contain prayers, praises to the gods, and their position in the Devaloka. In this, information about water therapy, air therapy, solar therapy, mental therapy, and therapy by Havan, etc. is also available.
Yajurveda
Yaju means dynamic sky and karma. Yajurveda contains the methods of Yajna and the mantras used in Yajna. Apart from Yagya, there is a description of philosophy. Philosophy means mysterious knowledge. Knowledge of the universe, soul, God, and matter. There are 2 branches of this Veda – Shukla and Krishna.
Samaveda
Sama means transformation and music. Gentleness and worship. In this Veda, there is a musical form of hymns of Rigveda. In this, there is mention of Savita, Agni, and Indra deities. This is also the mention of classical music and dance. This Veda is considered to be the root of music science. It also describes the science and psychology of music.
Atharvveda
Therva means vibration and Atharva means non-vibration. In this Veda, there is mention of mysterious knowledge, herbs, miracles, Ayurveda, etc. In this, knowledge of Indian tradition and astrology is also available.
Sanhita
Mantra Sahita, the mantras of the Vedas are full of beauty. When Vedic sages recite Veda mantras with voice, the mind becomes happy. Whoever listens to the recitation of Vedas, gets mesmerized.
Brahmin
The Brahmin texts mainly deal with Yagyas. There is an explanation of the mantras of the Vedas. There is a detailed description of the law and science of Yagyas. The main Brahmins are 3- (1) Aitareya, (2) Taittiriya, and (3) Shatpath.
Aranyaka
Forest is called ‘Aranya’ in Sanskrit. The books that originated in Aranya were named ‘Aranyaka’. The main Aranyakas are 5- (1) Aitareya, (2) Shankhayana, (3) Brihadaranyak, (4) Taittiriya and (5) Tavalkar.
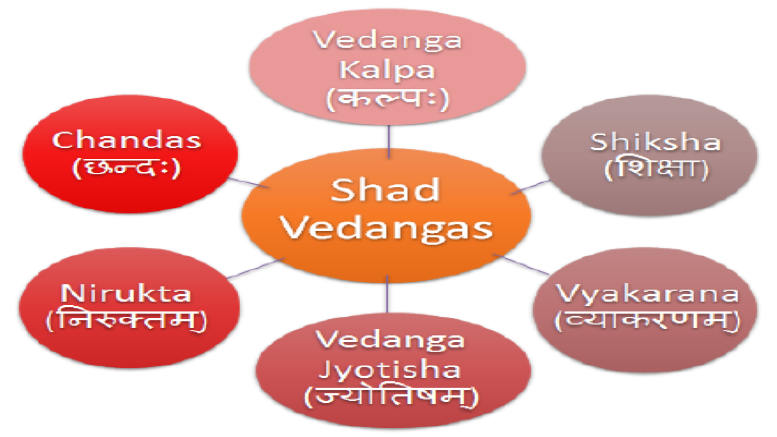
6 Vedanga
(1) Education, (2) Verse, (3) Grammar, (4) Nirukta, (5) Astrology, and (6) Kalpa.
6 Upang
(1) Pratipadasutra, (2) Anupada, (3) Verse language (Pratishakhya), (4) Dharmashastra, (5) Nyaya and (6) Vaisheshika. These 6 appendices are available. This is called Shaddarshan, which is like this – Sankhya, Yoga, Nyaya, Vaisheshik, Mimansa, and Vedanta.
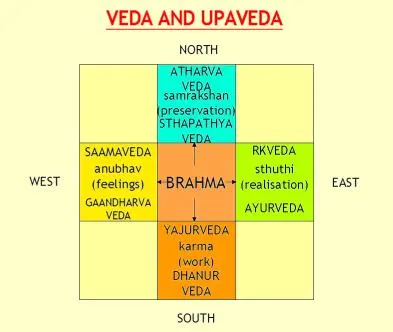
Upavedas of Vedas
Ayurveda of Rigveda, Dhanurveda of Yajurveda, Gandharvaveda of Samaveda, and Sthapatya Veda of Atharvaveda – these have been described as Upavedas of the four Vedas respectively.
.1. Dhanvantari, the doer of Ayurveda.
2. Vishwamitra, the doer of Dhanurveda.
3.Narad Muni, the doer of Gandharvaveda.
4.Vishwakarma is the doer of Sthapatyaveda.
What is Upanishad?
The Upanishads are the essence of the Vedas. Abstract means to squeeze or brief. The Upanishads are the basic foundation of Indian spiritual thought and the source of Indian spiritual philosophy. Whether there is God or not, whether there is a soul or not, how the universe is, etc. all serious, philosophy, yoga, meditation, samadhi, salvation, etc. will be found in the Upanishads. Upanishads should be read by every Hindu. Reading these gives true knowledge about God, the soul, salvation, and the world.
The last part of the Vedas is called ‘Vedanta‘. Only Vedanta is called Upanishad. Philosophy is discussed in the Upanishads. Although the number of Upanishads is 108, the main 12 are considered, such as- 1. Ish, 2. Ken, 3. Kath, 4. Prashna, 5. Mundak, 6. Mandukya, 7. Taittiriya, 8. Aitareya, 9 .Chhandogya, 10. Brihadaranyaka, 11. Kaushitaki and 12. Shvetashvatara.

What is a Shaddarshan ?
Shaddarshan emerged from Vedas: 6 sages created their philosophy only after reading the Vedas and Upanishads. This is called the Conspiracy of India. It is a categorization of the knowledge of the Vedas. These 6 philosophies are- 1. Nyaya, 2. Vaiseshik, 3. Sankhya, 4. Yoga, 5. Mimansa and 6. Vedanta. According to the Vedas, truth or God cannot be known through any one medium. That is why Vedas have discussed many paths or mediums.

What is there in Gita?
Gita is part of Bhishma Parva, one of the 18 chapters of the Mahabharata. There are 18 chapters in Gita as well. The total number of verses in 10 chapters is 700. If anyone has arranged the knowledge of Vedas in a new way, then it is Lord Krishna. Hence the pocket version of the Vedas is the Gita, which is the only universally accepted scripture of the Hindus. No one has enough time to read the Vedas or Upanishads. For them, the best scripture is the Gita. It is only after reading the Gita again and again that it starts to make sense.

The path of devotion, knowledge, and action has been discussed in the Gita. It has also been told about Yama-Niyama and Dharma-Karma. The Gita itself says that Brahma (God) is only one. If you read Gita again and again, the secret of its knowledge will be revealed to you. A separate book can be written on each word of the Gita.
In Gita creation origin, organism development order, Hindu messenger order, human origin, yoga, religion-karma, God, God, Goddess-Goddess, worship, prayer, Yama-rule, politics, war, salvation, space, sky, earth, Sanskar, dynasty, clan, policy, meaning, previous birth, life management, nation building, soul, the principle of action, the concept of three gunas, friendship among all beings, etc. are all known. Shrimad Bhagwadgita is the speech of Yogeshwar Shri Krishna. There is light of knowledge in each of its verses, as soon as it emerges, the darkness of ignorance is destroyed. Knowledge-Bhakti-Karma Yoga paths have been explained in detail. By following these paths, a person becomes entitled to the supreme position. Apart from Arjuna, Sanjay heard the Gita and narrated it to Dhritarashtra. In Gita, Shri Krishna has said 574 verses, Arjuna 85, Sanjay 40, and Dhritarashtra 1 verse.
Major Hindu books and writers
- Ashtadhyayi – Panini
- Ramayana – Valmiki
- Mahabharata – Vedvyas
- Ashtasahastrik Sutra, Prajnaparamita Sutrashastra, Madhyamika Sutra – Nagarjuna
- Buddhacharit, Sariputra Episode, Sutralankar Vajrasuchi, Soundaryanand, Shraddhotpad – Ashwaghosh
- Mudrarakshasa, Devi Chandragupta – Visakhadatta
- Economics – Chanakya
- Mahabhashya – Patanjali
- Kumarasambhavam, Abhijnanasakuntalam, Vikramorvashiyam, Meghdootam, Raghuvansham, Malavikagnimitram, Ritusamharam – Kalidas
- Swapnavasavadattam, PratigyaYogandharayan – Bhas
- Nagananda, Ratnavali, Priyadarshika – Harshvardhan
- Harshacharit, Kadambari – Banabhatta
- Vikramank Charit – Bilhan
- Prithviraj Raso – Chandbardai
- Rajatarangini – Kalhana
- Chaurapanchashika – Bilhan
- Rasmala, Kirti Kaumudi – Someshwar
- Karpoormanjari – Rajasekhar
- Indica – Magasthenes
- Charaka Samhita – Charaka
- Sushruta Samhita – Sushruta
- Mricchakatikam – Shudraka
- Sangeet Ratnakar – Shangrgadev
- Mitakshara – Vigyaneshwar
- Kiratarjuniyam – Bharavi
- Panchatantra – Vishnu Sharma
- Nyaya Bhashya, Kamasutra – Vatsyayana
- Kavyadarsh, Dashkumarcharit – Dandi
- Vasavadatta – Subandhu
- Surya Siddhanta – Aryabhatta
- Brihat Samhita, Pancha Siddhantika, Brihajjatika, Laghujatika – Varahmihir
- Gitagovindam – Jayadeva
- Anargharaghava – Murari
- Ayurveda Sarvasva, Rajmartand, Behavior set, Word discipline, Yuktikalpataru, Rajmrigika – Raja Bhoj
- Bhojprabandh – Ballal
- Shishupala slaughter – Magha
- Naishadhiyacharitam – Sri Harsha
- Malati Madhav, Mahavir Charit, Uttarramcharit – Bhavabhuti
- Literary Mirror:- Bhamah
- Dhvanyalok:, Pramodchandra – Anandvardhan
- Individual discretion: – Mahimbhatta
- Kavyadarsh – Mammat
- Venisamhara – Bhatt Narayan
- Pramana Mimansa – Hemchandra
- Brihatkathamanjari – Kshemendra
- Katantra (Grammar) – Sarvavarman
- Ashtangasamgraha, Siddhanta Shiromani, Lilavati (first book of algebra) – Bhaskaracharya
- Madhav Nidan – Madhavkar
- Nighantu – Yasak
- Rasaratnakar – Nagarjuna
- Tattva Kaumudi, Tattva Shardi, Nyayavartika, Nyayasutra Dhara, Nyayakanika, Yogasarasangraha – Vachaspati Mishra
- Yogavartika, Yogasarasamgra – Science monk
- Tilakmanjari, Yashstilak – Dhanapal
- Kuttanimatam – Damodar Gupta
- Tattvashuddhi – Udayan
- Justice – Jayant
- Nyayatattva Yogarahasya – Nathmuni
- Song collection, great Man decision, Siddhatraya, Agam Pramanya – Yamunacharya
- Dhurtavyama, Samraditya Katha – Haribhadra
- Kuvalayamala – Udyotanasuri
- Ajit Shantistava – Nandisen
- Satsai – Hall
- Brihatkatha – Gunadhya